Mapping (float)
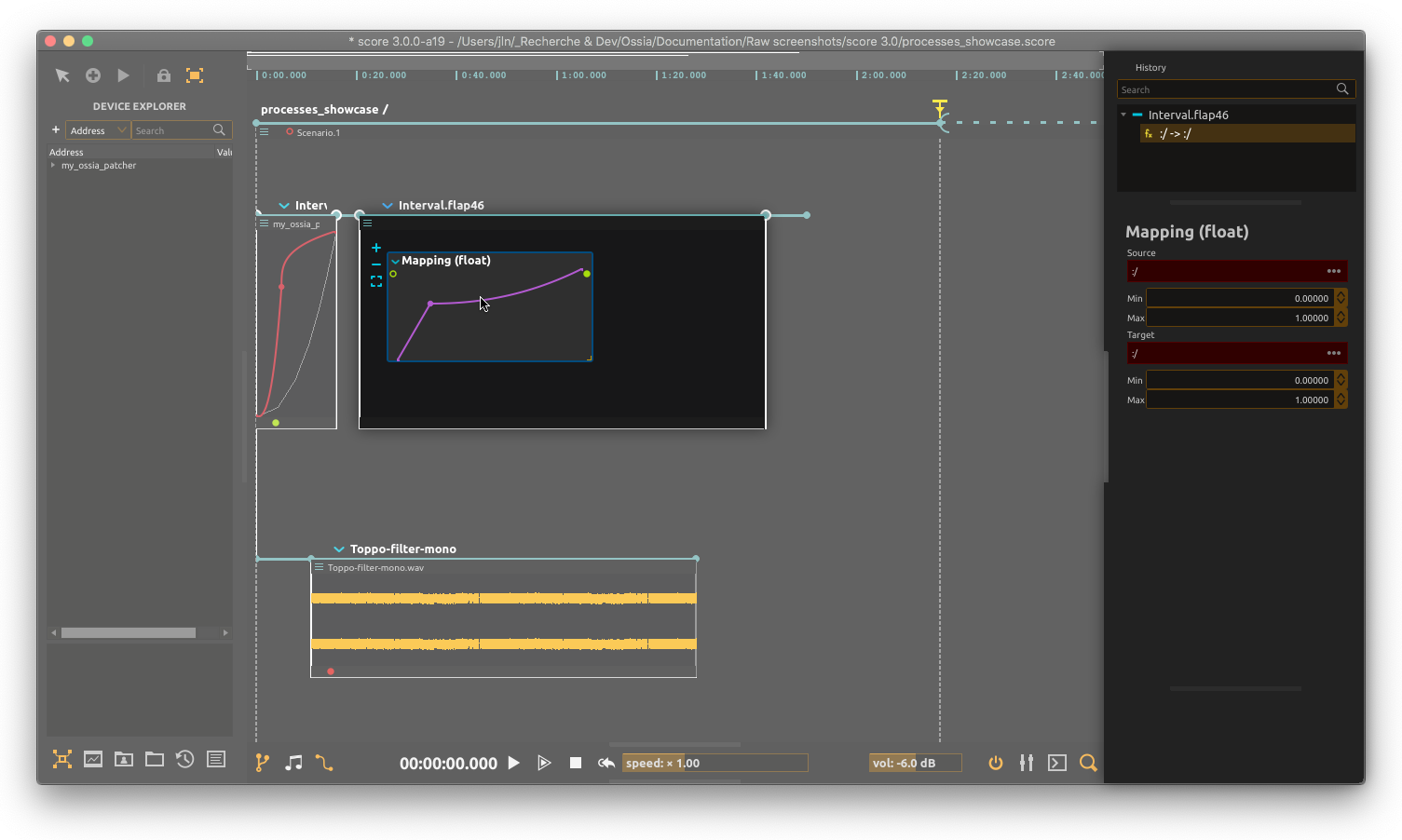
This process allows to map a float value to another, by following a transfer curve. The inspector allows to choose the expected range for input and output values.
Example
Consider the following setup:
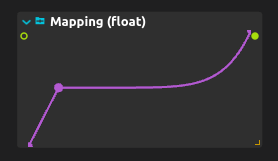
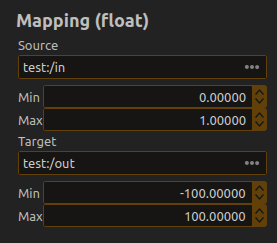
When a value gets into the mapping input, it is mapped as if it was a value of the horizontal axis of the diagram, where 0 is the left and 1 is at the right, to the value of the curve being drawn, where the bottom of the process is at -100 and the top of the process is at 100.
Here are a table of some of the (approximative) outputs for various inputs in the above case:
- input = 0 => output = -100
- input = 0.1 => output = -50
- input = 0.2 => output = 0
- input = 0.3 => output = 0
- input = 0.4 => output = 0
- input = 0.5 => output = 1
- …
- input = 0.8 => output = 10
- input = 0.9 => output = 50
- input = 1.0 => output = 100