Grid-Based Amplitude Panning (GBAP)
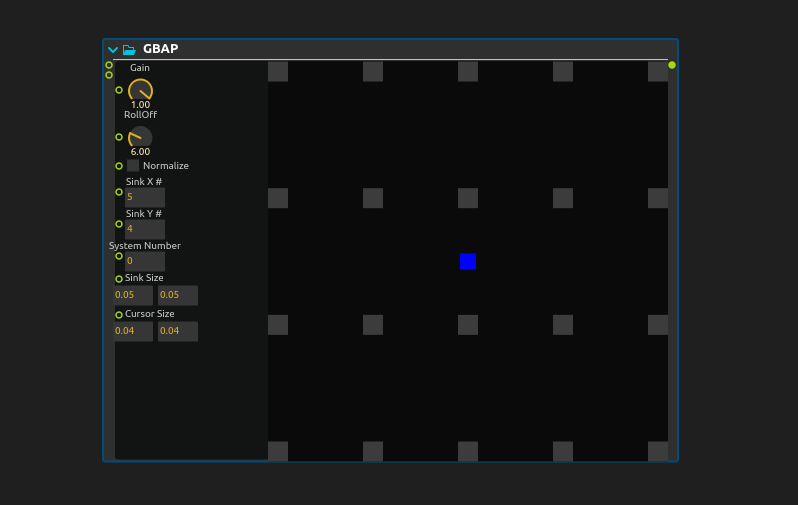
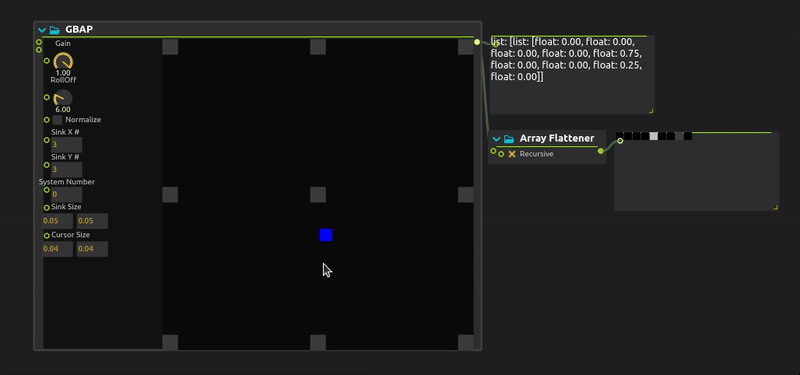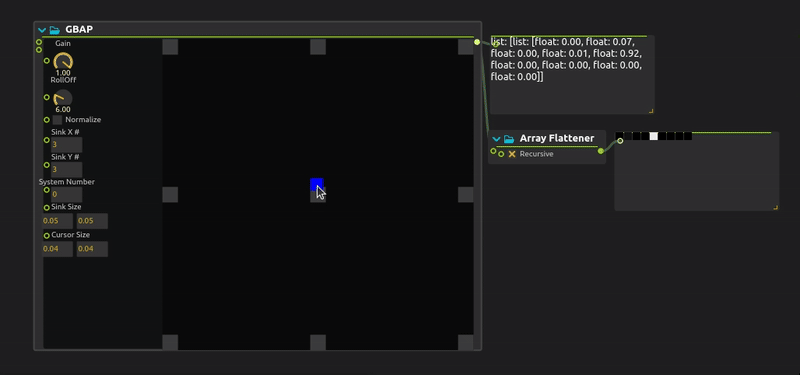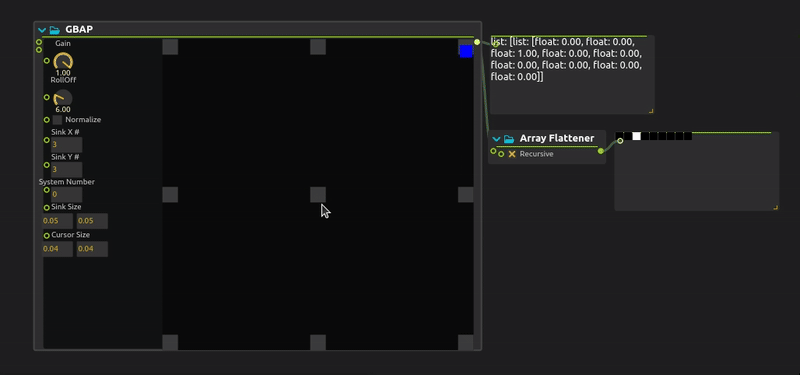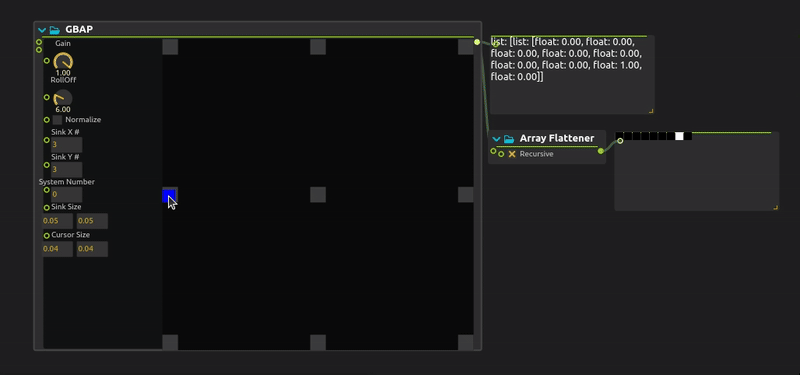
GBAP (Grid-Based Amplitude Panning) is a spatial audio technique that distributes sound across a regular grid of speakers or virtual sound sources. It calculates amplitude weights based on the proximity of a sound source to grid points, enabling intuitive 2D spatialization for installations, concerts, and immersive audio environments.
Moving cursor
- The cursor can be dragged in 2D space using the mouse. It is also possible to click on an empty area to move the cursor.
Parameters
-
Gain : Gain parameter adjusts the maximum volume of the various sinks.
-
Roll Off : Roll Off parameter shapes how the amplitude decays across the grid. A higher roll-off value emphasizes the closest sinks while reducing the influence of distant ones.
-
Normalize : When enabled, the volume values are normalized so that the highest value equals 1. This ensures the panning keeps consistent energy regardless of the number of affected sinks.
-
Sink (X or Y) # : Defines how many sinks (speakers/outputs) are placed horizontally (
X) and vertically (Y) in the 2D grid. -
Sinks Size : Sets the size (width and height) of each sink’s influence zone in the grid. Larger sizes make sinks cover more area.
-
Cursor Size : Represents the area of influence (e.g., a sound source) within the grid. Bigger cursors affect more sinks, resulting in broader spatial panning.
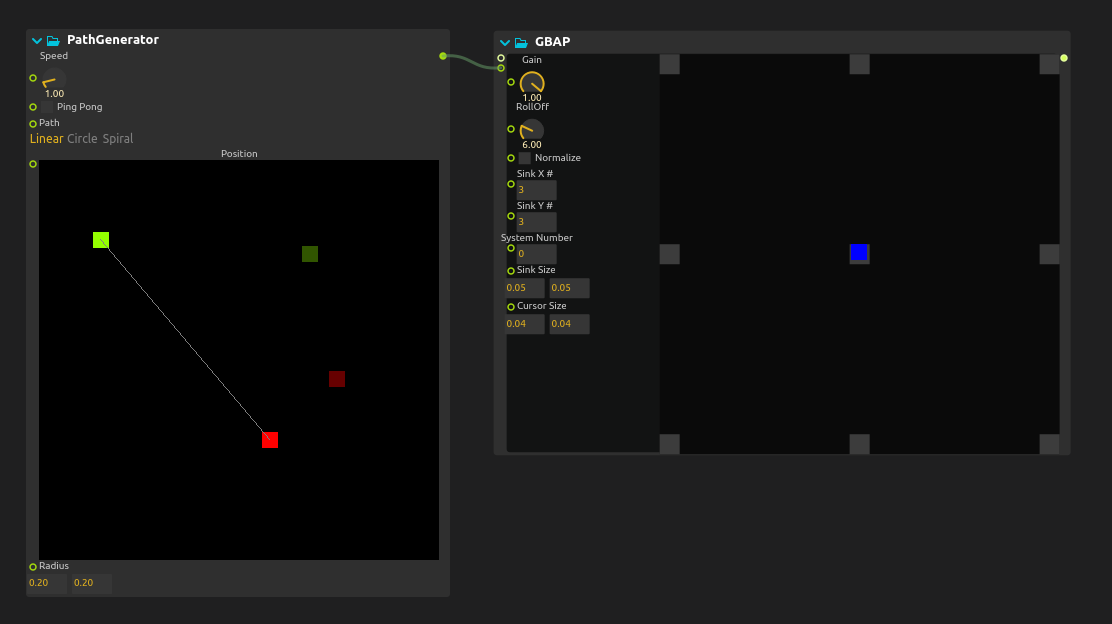
How to add a multicursor or an path
To allow even more creative possibilities in sound spacialization, it is possible to integrate multiple sources and automatic trajectories thanks to MultiCursor and PathGenerator.
To do this, when your Multicursor and Pathgenerator are set up, connect its output array to the second GBAP input.
NOTE : When an external panel is connected to the GBAP. The array integrated in the gbap is no longer taken into account and therefore has no effect on the final result.
Inputs and Outputs
| Port | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cursor Position | Vec2 | X,Y position of the sound source |
| External Cursors | Array | Array of cursor positions from Multi-Cursor or Path Generator |
| Port | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Gains | Float Array | Amplitude coefficients for each grid point/speaker |
| Visual | Object | Grid state for visual feedback |
Usage Examples
Basic Spatialization Setup
- Add GBAP Process: Drag GBAP from Process Library
- Configure Grid: Set X and Y sink count for your speaker layout
- Connect Audio: Route through Matrix process to speakers
- Control Position: Use mouse, MIDI, or sensors
[Audio Source] → [Matrix] → [Speaker 1-4]
↑
[GBAP Gains] ←── [Cursor Control]
Automated Movement
Create automatic spatial trajectories:
[LFO X] → [Combine] → [GBAP] → [Speaker Gains]
[LFO Y] →
Interactive Installation
Use sensor data for positioning:
[Motion Sensor] → [Scale/Filter] → [GBAP] → [Multi-Speaker Array]
Integration with Other Processes
With Multi-Cursor
Create multiple simultaneous sound sources:
[Multi-Cursor] → [GBAP] → [Combined Gains] → [Speaker Array]
With Path Generator
Automate complex spatial trajectories:
[Path Generator] → [GBAP] → [Trajectory Gains] → [Immersive Audio]
With Audio Sources
Complete spatialization chain:
[Multiple Sources] → [Audio Router] → [GBAP Processing] → [Physical Speakers]
↑
[Position Controllers]
Best Practices
- Grid Size: Match grid dimensions to your physical speaker layout
- Cursor Size: Larger cursors create smoother, wider spatialization
- Normalization: Enable for consistent energy across positions
- Roll-off: Tune for your room acoustics and desired focus
- Real-time: GBAP is optimized for real-time performance
Troubleshooting
- No output: Check Matrix routing and speaker connections
- Harsh transitions: Increase cursor size or reduce roll-off
- Uneven levels: Enable normalization
- Performance: Reduce grid size for complex setups
Related Processes
- DBAP - Distance-based panning for irregular layouts
- Matrix - Audio routing and mixing
- Multi-Cursor - Multiple position sources
- Path Generator - Automated trajectories