CoAP Device
CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) is a specialized web transfer protocol designed for use with constrained nodes and networks in the Internet of Things (IoT). It is a standard internet protocol closely related to HTTP in behavior and operations, but with much more efficient communication optimized for resource-limited devices.
Overview
CoAP is designed for:
- Constrained devices with limited processing power and memory
- Lossy networks with high packet loss and low bandwidth
- Battery-powered devices requiring energy-efficient communication
- Machine-to-machine (M2M) communication in IoT ecosystems
- Embedded control systems and sensor networks
Key CoAP features:
- UDP-based for low overhead (default port: 5683)
- RESTful architecture similar to HTTP but optimized for constraints
-
Built-in discovery mechanism via
/.well-known/core - Observe pattern for real-time data subscription
- Block-wise transfers for handling large payloads
Supported Transports
ossia score supports all standard CoAP transports:
UDP (Default)
- Lightweight, connectionless communication
- Best for battery-powered and resource-constrained devices
- Port 5683 (5684 for DTLS secure connections)
TCP
- Reliable, connection-oriented communication
- Better for stable network connections
- Useful when message ordering is critical
WebSocket
- CoAP over WebSocket transport
- Browser compatibility and firewall traversal
- Integration with web-based systems
Device Setup & Discovery
Basic Configuration
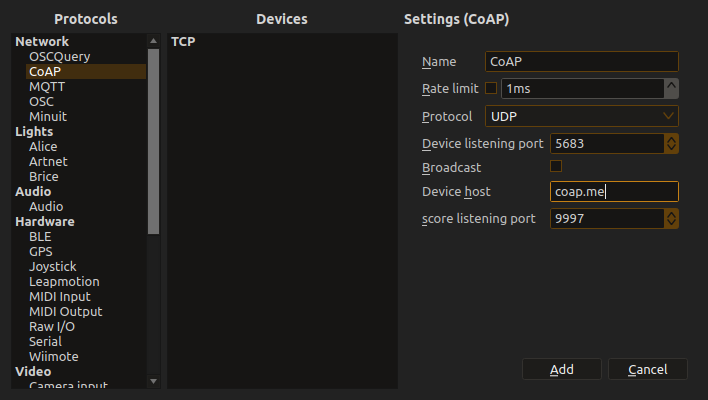
- Add CoAP Device: Right-click Device Explorer → Add Device → CoAP
-
Configure Connection:
-
Host: Target device IP address (e.g.,
192.168.1.100) - Port: CoAP port (5683 for UDP, custom for others)
- Transport: UDP, TCP, or WebSocket
-
Host: Target device IP address (e.g.,
CoAP’s discovery mechanism then automatically finds available resources which get exposed as ossia device explorer nodes.
Practical Examples
Public CoAP Testing
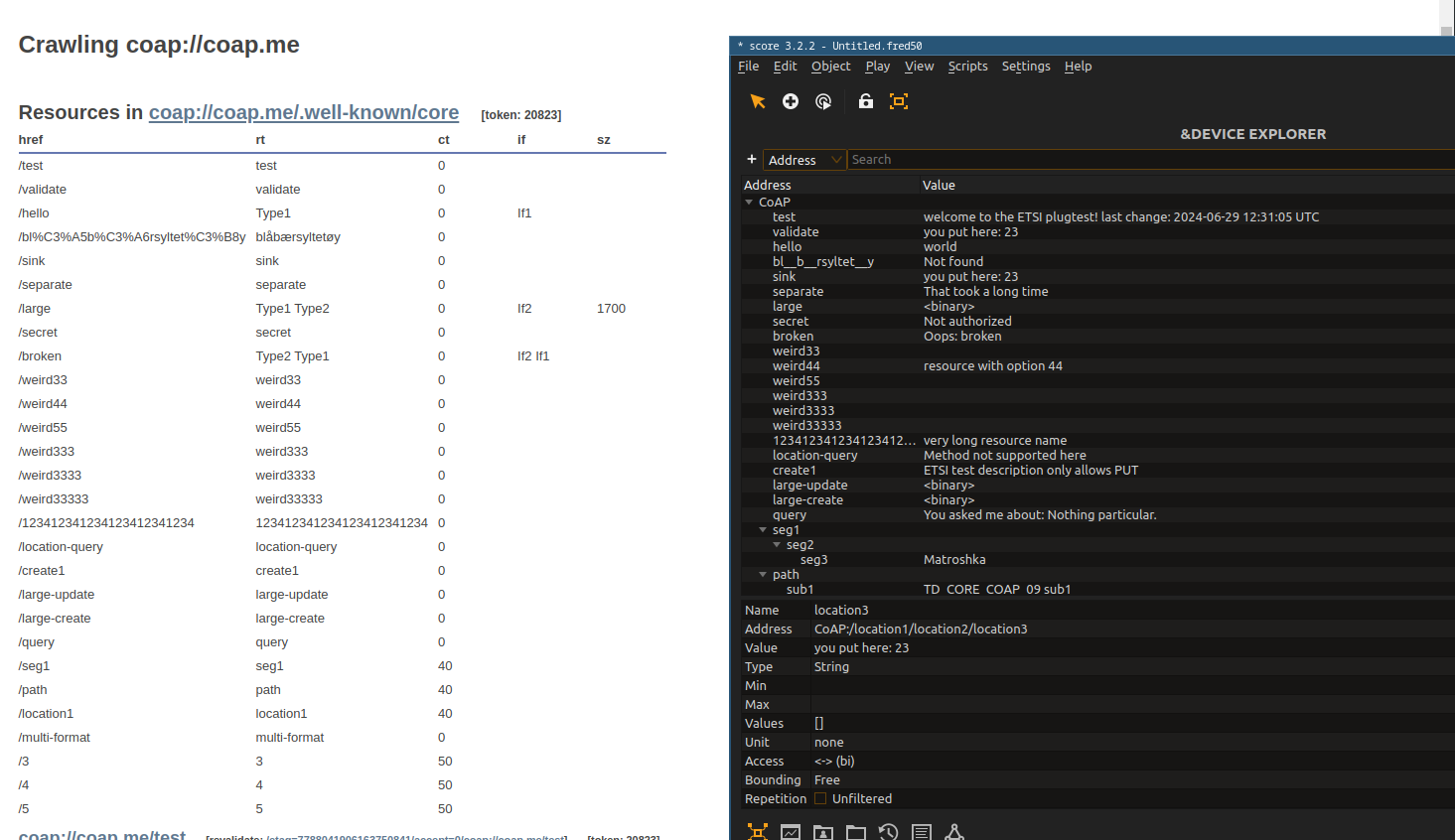
Try with the public CoAP server at coap.me:
-
Add CoAP Device with host
coap.me, port5683, UDP transport -
Explore resources like
/hello,/time,/separate - Test OBSERVE on resources that support real-time updates
Troubleshooting
Connection Issues
- Verify port 5683 accessibility through firewalls
- Check device IP address and network connectivity
- Test with CoAP tools (coap-client, Copper browser plugin)
- Monitor UDP packet loss on unreliable networks
Discovery Problems
-
Check
/.well-known/coreendpoint responds correctly - Validate link format syntax in discovery responses
- Try manual resource addition if auto-discovery fails
- Verify content-type headers in discovery responses
Related Documentation
- MQTT Device - Alternative IoT messaging protocol
- HTTP Device - Full-featured query-based web protocol
- WS Device - Full-featured streaming web protocol
- OSC Device - Real-time multimedia control